Species of Thailand
Burmese python
Python bivittatus
Heinrich Kuhl, 1820
In Thai: งูหลาม, ngu laam
The Burmese python (Python bivittatus) is one of the largest species of snakes. It is native to a large area of Southeast Asia and is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Until 2009, it was considered a subspecies of the Indian python, but is now recognized as a distinct species. It is an invasive species in Florida as a result of the pet trade.
Description
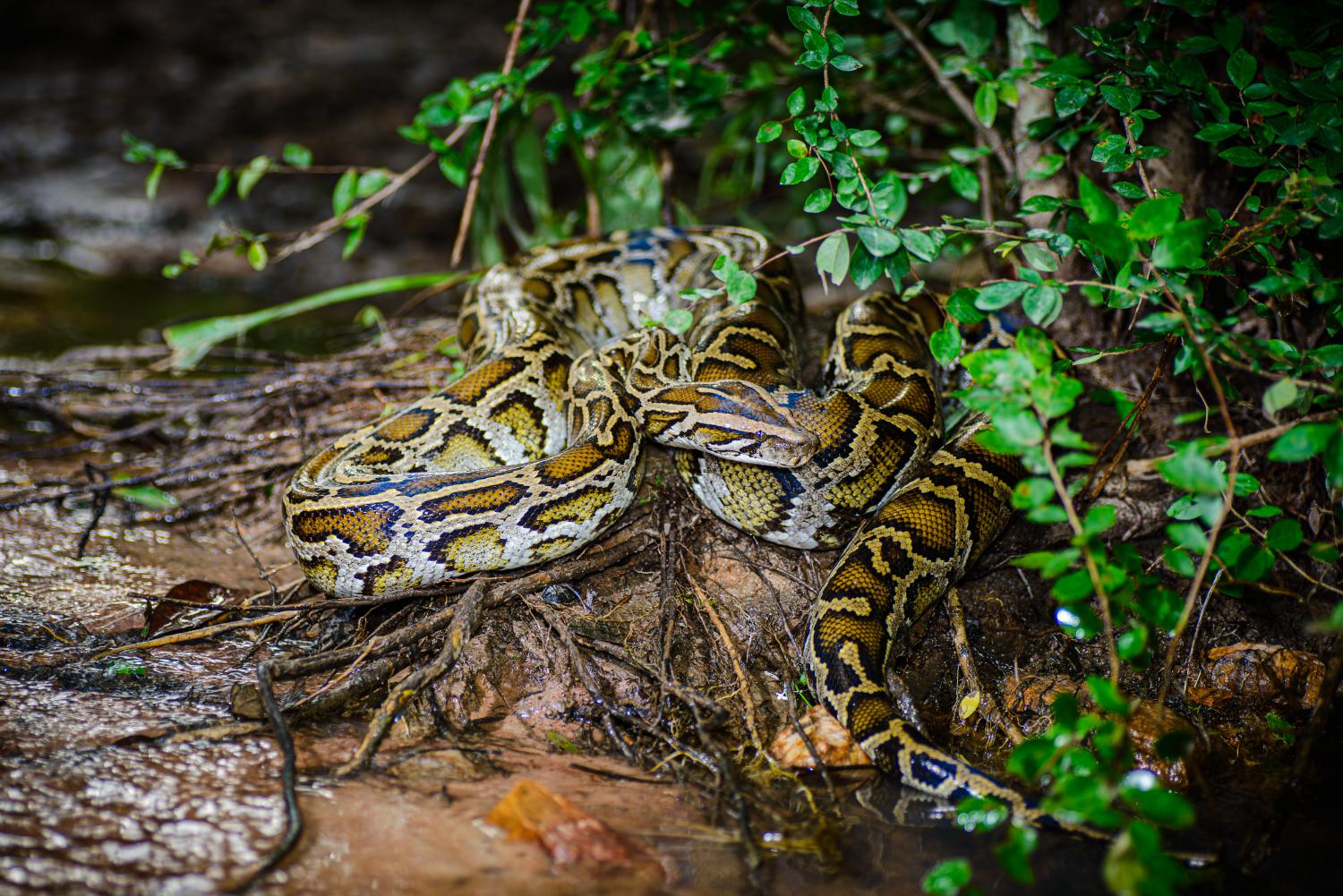
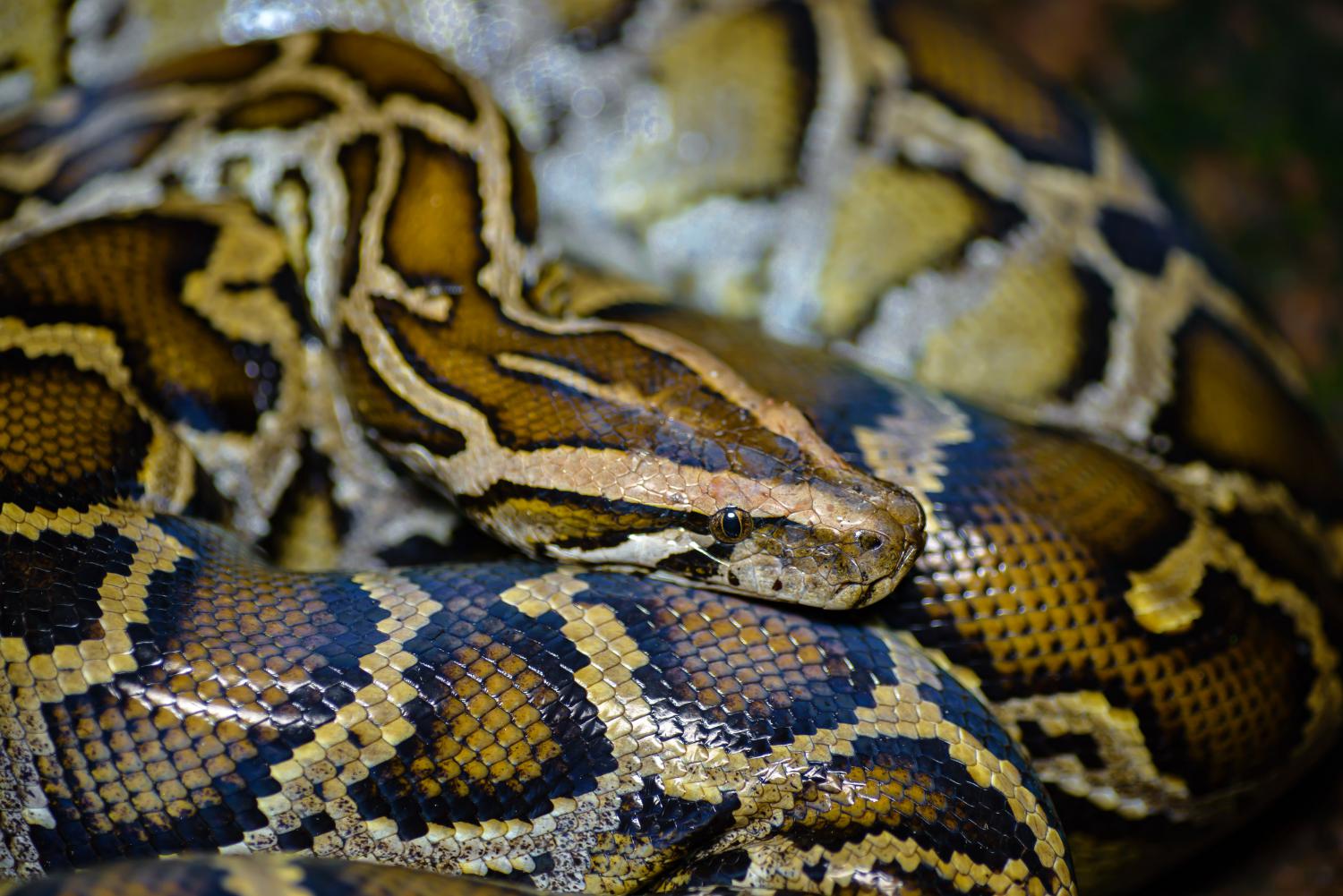
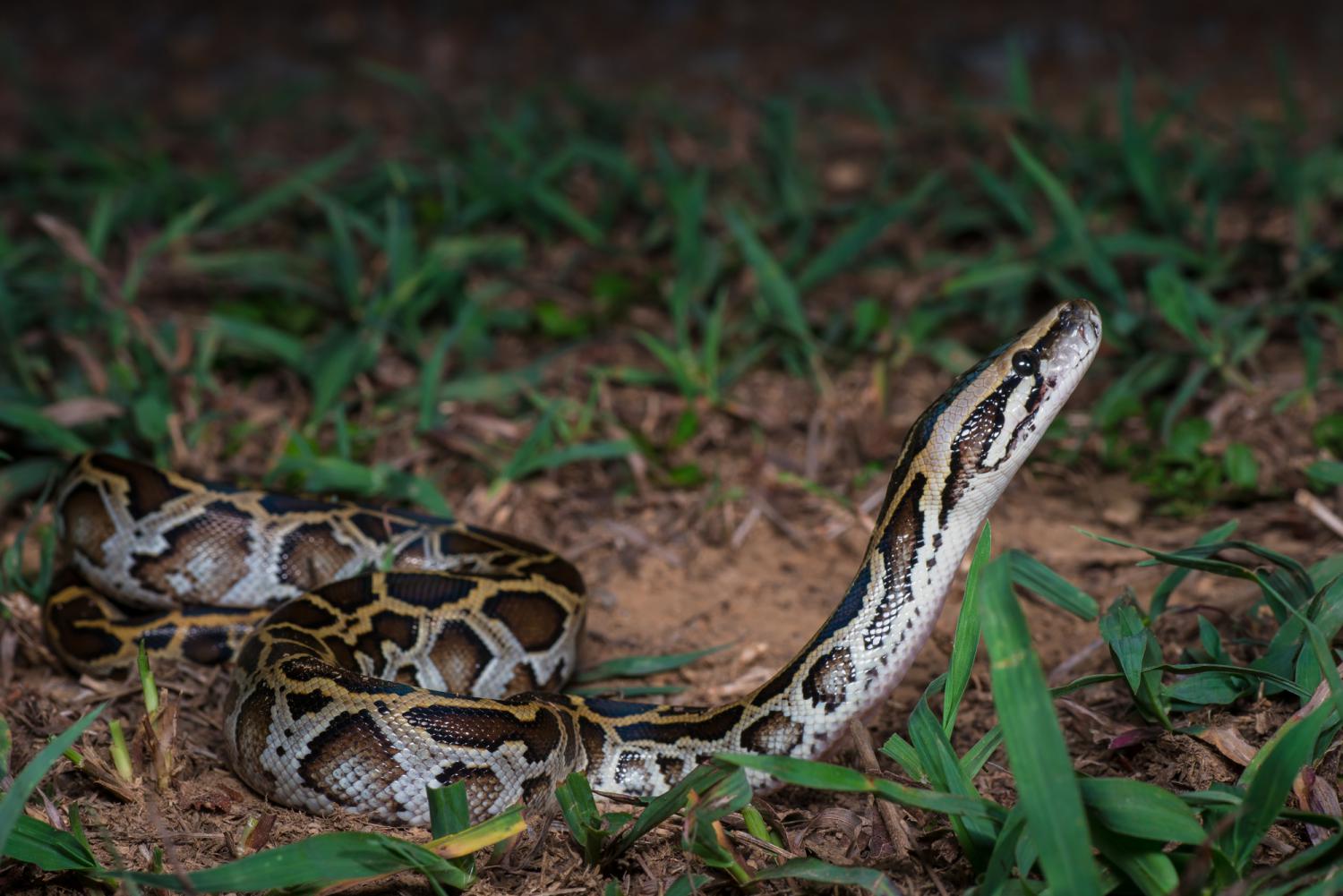
The Burmese python is a dark-colored non-venomous snake with many brown blotches bordered by black down the back.
In the wild, Burmese pythons typically grow to 5 m, while specimens of more than 7 m are unconfirmed. This species is sexually dimorphic in size; females average only slightly longer, but are considerably heavier and bulkier than the males. For example, length-weight comparisons in captive Burmese pythons for individual females have shown: at 3.47 m length, a specimen weighed 29 kg, a specimen of just over 4 m weighed 36 kg, a specimen of 4.5 m weighed 40 kg, and a specimen of 5 m weighed 75 kg. In comparison, length-weight comparisons for males found: a specimen of 2.8 m weighed 12 kg, 2.97 m weighed 14.5 kg, a specimen of 3 m weighed 7 kg, and a specimen of 3.05 m weighed 18.5 kg. In general, individuals over 5 m are rare. The record for maximum length of Burmese pythons is 5.79 m and was caught 10 July 2023 in South Florida's Big Cypress National Preserve. Widely published data of specimens reported to have been several feet longer are not verified. At her death, a Burmese named "Baby" was the heaviest snake recorded in the world at the time at 182.8 kg, much heavier than any wild snake ever measured. Her length was measured at 5.74 m ftin circa 1999. The minimum size for adults is 2.35 m. Dwarf forms occur in Java, Bali, and Sulawesi, with an average length of 2 m in Bali, and a maximum of 2.5 m on Sulawesi. Wild individuals average 3.7 m long, but have been known to reach 5.79 m.
Diseases
In both their native and invasive range they suffer from Raillietiella orientalis (a pentastome parasitic disease).
Distribution and habitat
The Burmese python occurs throughout Southern and Southeast Asia, including eastern India, southeastern Nepal, western Bhutan, southeastern Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, northern continental Malaysia, and southern China in Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangdong, Hainan, Guangxi, and Yunnan. It also occurs in Hong Kong, and in Indonesia on Java, southern Sulawesi, Bali, and Sumbawa. It has also been reported in Kinmen.
It is an excellent swimmer and needs a permanent source of water. It lives in grasslands, marshes, swamps, rocky foothills, woodlands, river valleys, and jungles with open clearings. It is a good climber and has a prehensile tail. It can stay in water for 30 minutes but mostly stays on land.
As an invasive species
Python invasion has been particularly extensive, notably across South Florida, where a large number of pythons can now be found in the Florida Everglades. Between 1996 and 2006, the Burmese python gained popularity in the pet trade, with more than 90, 000 snakes imported into the U.S. The current number of Burmese pythons in the Florida Everglades may have reached a minimum viable population and become an invasive species. Hurricane Andrew in 1992 was deemed responsible for the destruction of a python-breeding facility and zoo, and these escaped snakes spread and populated areas into the Everglades. More than 1, 330 have been captured in the Everglades. A genetic study in 2017 revealed that the python population is composed of hybrids between the Burmese python and Indian python. The species also displays cytonuclear discordance which has made phylogenetic studies of its origin more complicated.
By 2007, the Burmese python was found in northern Florida and in the coastal areas of the Florida Panhandle. The importation of Burmese pythons was banned in the United States in January 2012 by the U.S. Department of the Interior. A 2012 report stated, "in areas where the snakes are well established, foxes, and rabbits have disappeared. Sightings of raccoons are down by 99.3%, opossums by 98.9%, and white-tailed deer by 94.1%." Road surveys between 2003 and 2011 indicated an 87.3% decrease in bobcat populations, and in some areas rabbits have not been detected at all. Experimental efforts to reintroduce rabbit populations to areas where rabbits have been completely eliminated have mostly failed "due to high (77% of mortalities) rates of predation by pythons." Bird and coyote populations may be threatened, as well as the already-rare Florida panther. In addition to this correlational relationship, the pythons have also been experimentally shown to decrease marsh rabbit populations, further suggesting they are responsible for many of the recorded mammal declines. They may also outcompete native predators for food.
For example, Burmese pythons also compete with the native American alligator, and numerous instances of alligators and pythons attacking—and in some cases, preying on—each other have been reported and recorded.
By 2011, researchers identified up to 25 species of birds from nine avian orders in the digestive tract remains of 85 Burmese pythons found in Everglades National Park. Native bird populations are suffering a negative impact from the introduction of the Burmese python in Florida; among these bird species, the wood stork is of specific concern, now listed as federally endangered.
Numerous efforts have been made to eliminate the Burmese python population in the last decade. Understanding the preferred habitat of the species is needed to narrow down the python hunt. Burmese pythons have been found to select broad-leafed and low-flooded habitats. Broad-leafed habitats comprise cypress, overstory, and coniferous forest. Though aquatic marsh environments would be a great source for prey, the pythons seem to prioritize environments allowing for morphological and behavioral camouflage to be protected from predators. Also, the Burmese pythons in Florida have been found to prefer elevated habitats, since this provides the optimal conditions for nesting. In addition to elevated habitats, edge habitats are common places where Burmese pythons are found for thermoregulation, nesting, and hunting purposes.
One of the Burmese python eradication movements with the biggest influence was the 2013 Python Challenge in Florida. This was a month-long contest wherein a total of 68 pythons were removed. The contest offered incentives such as prizes for longest and greatest number of captured pythons. The purpose of the challenge was to raise awareness about the invasive species, increase participation from the public and agency cooperation, and to remove as many pythons as possible from the Florida Everglades. The challenge has run a few times again since then and is now an annual event over the duration of ten days. Recently, in 2023, it resulted in 209 pythons removed by 1, 050 participants.
A study from 2017 introduced a new method for identifying the presence of Burmese pythons in southern Florida; this method involves the screening of mosquito blood. Since the introduction of the Burmese python in Florida, mosquito communities use the pythons as hosts even though they are recently introduced.
Invasive Burmese pythons also face certain physiological changes. Unlike their native South Asian counterparts who spend long periods fasting due to seasonal variation in prey availability, pythons in Florida feed year-round due to the constant availability of food. They are also vulnerable to cold stress, with winter freezes resulting in mortality rates of up to 90%. Genomic data suggests natural selection on these populations favors increased thermal tolerance as a result of these high-mortality freezes.
They have carried Raillietiella orientalis, a pentastome parasitic disease, with them from Southeast Asia. Other reptiles in Florida have become infested, and the parasite appears to have become endemic.
In April 2019, researchers captured and killed a large Burmese python in Florida's Big Cypress National Preserve. It was more than 5.2 m long, weighed 64 kg, and contained 73 developing eggs.
In December 2021, a Burmese python was captured in Florida that weighed 98 kg and had a length of 5.5 m it contained a record 122 developing eggs.
In July 2023, local hunters captured and killed a 5.8 m long Burmese python that weighed 57 kg kg in Florida's Big Cypress National Preserve.
Behavior
Burmese pythons are mainly nocturnal rainforest dwellers. When young, they are equally at home on the ground and in trees, but as they gain girth, they tend to restrict most of their movements to the ground. They are also excellent swimmers, being able to stay submerged for up to half an hour. Burmese pythons spend the majority of their time hidden in the underbrush. In the northern parts of its range, the Burmese python may brumate for some months during the cold season in a hollow tree, a hole in the riverbank, or under rocks. Brumation is biologically distinct from hibernation. While the behavior has similar benefits, allowing organisms to endure the winter without moving, it also involves the preparation of both male and female reproductive organs for the upcoming breeding season. The Florida population also goes through brumation.
They tend to be solitary and are usually found in pairs only when mating. Burmese pythons breed in the early spring, with females laying clutches of 12–36 eggs in March or April. They remain with the eggs until they hatch, wrapping around them and twitching their muscles in such a way as to raise the ambient temperature around the eggs by several degrees. Once the hatchlings use their egg tooth to cut their way out of their eggs, no further maternal care is given. The newly hatched babies often remain inside their eggs until they are ready to complete their first shedding of skin, after which they hunt for their first meal.
Diet
Like all snakes, the Burmese python is carnivorous. Its diet consists primarily of birds and mammals, but also includes amphibians and reptiles. It is a sit-and-wait predator, meaning it spends most of its time staying relatively still, waiting for prey to approach, then striking rapidly. The snake grabs a prey animal with its sharp teeth, then wraps its body around the animal to kill it through constriction. The python then swallows its prey whole. It is often found near human habitation due to the presence of rats, mice, and other vermin as a food source. However, its equal affinity for domesticated birds and mammals means it is often treated as a pest. In captivity, its diet consists primarily of commercially available appropriately sized rats, graduating to larger prey such as rabbits and poultry as it grows. As an invasive species in Florida, Burmese pythons primarily eat a variety of small mammals including foxes, rabbits, and raccoons. Due to their high predation levels, they have been implicated in the decline and even disappearance of many mammal species. In their invasive range, pythons also eat birds and occasionally other reptiles. Exceptionally large pythons may even require larger food items such as pigs or goats, and are known to have attacked and eaten alligators and adult deer in Florida.
Digestion
The digestive response of Burmese pythons to such large prey has made them a model species for digestive physiology. Its sit-and-wait hunting style is characterized by long fasting periods in between meals, with Burmese pythons typically feeding every month or two, but sometimes fasting for as long as 18 months. As digestive tissues are energetically costly to maintain, they are downregulated during fasting periods to conserve energy when they are not in use. A fasting python has a reduced stomach volume and acidity, reduced intestinal mass, and a 'normal' heart volume. After ingesting prey, the entire digestive system undergoes a massive re-modelling, with rapid hypertrophy of the intestines, production of stomach acid, and a 40% increase in mass of the ventricle of the heart to fuel the digestive process. During digestion, the snake's oxygen consumption rises drastically as well, increasing with meal size by 17 to 40 times its resting rate. This dramatic increase is a result of the energetic cost of restarting many aspects of the digestive system, from rebuilding the stomach and small intestine to producing hydrochloric acid to be secreted in the stomach. Hydrochloric acid production is a significant component of the energetic cost of digestion, as digesting whole prey items requires the animal to be broken down without the use of teeth, either for chewing or tearing into smaller pieces. To compensate, once food has been ingested, Burmese pythons begin producing large amounts of acid to make the stomach acidic enough to turn the food into a semi-liquid that can be passed through to the small intestine and undergo the rest of the digestive process.
The energy cost is highest in the first few days after eating when these regenerative processes are most active, meaning Burmese pythons rely on existing food energy storage to digest a new meal. Overall, the entire digestive process from food intake to defecation lasts 8–14 days.
Conservation
The Burmese python is listed on CITES Appendix II. It has been listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 2012, as the wild population is estimated to have declined by at least 30% in the first decade of the 21st century due to habitat loss and over-harvesting.
To maintain Burmese python populations, the IUCN recommends increased conservation legislation and enforcement at the national and international levels to reduce harvesting across the snake's native range. The IUCN also recommends increased research into its population ecology and threats. In Hong Kong, it is a protected species under Wild Animals Protection Ordinance Cap 170. It is also protected in Thailand, Vietnam, China, and Indonesia. However, it is still common only in Hong Kong and Thailand, with rare to very rare statuses in the rest of its range.
In captivity
Burmese pythons are often sold as pets, and are made popular by their attractive coloration and apparently easy-going nature. However, they have a rapid growth rate, and can exceed 2.1 m ftin in length in a year if power fed. However this may cause health issues in the future. By age four, they will have reached their adult size, though they continue growing very slowly throughout their lives, which may exceed 20 years.
Although the species has a reputation for docility, they are very powerful animals – capable of inflicting severe bites and even killing by constriction. They also consume large amounts of food, and due to their size, require large, often custom-built, secure enclosures. As a result, some are released into the wild, and become invasive species that devastate the environment. For this reason, some jurisdictions (including Florida, due to the python invasion in the Everglades) have placed restrictions on the keeping of Burmese pythons as pets. Violators could be imprisoned for more than seven years or fined $500, 000 if convicted.
Burmese pythons are opportunistic feeders; they eat almost any time food is offered, and often act hungry even when they have recently eaten. As a result, they are often overfed, causing obesity-related problems to be common in captive Burmese pythons.
Like the much smaller ball python, Burmese pythons are known to be easygoing or timid creatures, which means that if cared for properly, they can easily adjust to living near humans.
Handling
Although pythons are typically afraid of people due to their great stature, and generally avoid them, special care is still required when handling them. Given their adult strength, multiple handlers (up to one person per meter of snake) are usually recommended. Some jurisdictions require owners to hold special licenses, and as with any wild animal being kept in captivity, treating them with the respect an animal of this size commands is important.
Variations
The Burmese python is frequently captive-bred for color, pattern, and more recently, size. Its amelanistic form is especially popular and is the most widely available morph. This morph is white with patterns in butterscotch yellow and burnt orange. Also, "labyrinth" specimens with maze-like patterns, khaki-colored "green", and "granite" with many small angular spots are available. Breeders have recently begun working with an island lineage of Burmese pythons. Early reports indicate that these dwarf Burmese pythons have slightly different coloring and pattern from their mainland relatives and do not grow much over 2.1 m ftin in length. One of the most sought-after of these variations is the leucistic Burmese. This particular variety is very rare, being entirely bright white with no pattern and blue eyes, and has only in 2008/2009 been reproduced in captivity as the homozygous form (referred to as "super" by reptile keepers) of the co-dominant hypomelanistic trait. The caramel Burmese python has a caramel-colored pattern with "milk-chocolate" eyes.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Subphylum
- Vertebrata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Squamata
- Suborder
- Serpentes
- Family
- Pythonidae
- Genus
- Python
- Species
- Python bivittatus
Common names
- German: Dunkler Tigerpython
- English: Burmese python
- Thai: งูหลาม, ngu laam
Subspecies
Python bivittatus bivittatus, Heinrich Kuhl, 1820
Range: South Nepal, India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, South China, Indonesia (Java, Bali), USA (Introduced to Florida).
Python bivittatus progschai, Hans J. Jacobs, Mark Auliya, 2009
Range: Sulawesi
Synonyms
- Python bivittatus, Van Stanley Bartholomew Wallach et al. (2014)
- Python bivittatus progschai, Koch (2011)
- Python bivittatus progschai, Hans J. Jacobs, Mark Auliya & Wolfgang Böhme (2009)
- Python bivittatus, Hans J. Jacobs et al. (2009)
- Python molurus bivittatus, Tanya Chan-Ard et al. (1999)
- Python molurus bivittatus, Merel J. Cox et al. (1998)
- Python molurus bivittatus, Ulrich Manthey & Wolfgang Grossmann (1997)
- Python molurus bivittatus, Robert Mertens (1921)
- Python bivittatus, Heinrich Kuhl (1820)
- Python molurus bivittatus, Kuhl (1820)
Conservation status
Vulnerable (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review our species pages if wrong photos are used or any other details in the page is wrong. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
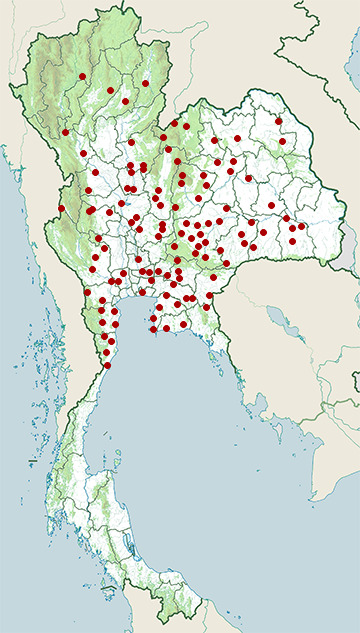
- Akat Amnuai District, Sakon Nakhon
- Ban Mi District, Lopburi
- Ban Pong District, Ratchaburi
- Ban Sang District, Prachinburi
- Bang Krathum District, Phitsanulok
- Bang Lamung District, Chonburi
- Bang Len District, Nakhon Pathom
- Bang Mun Nak District, Phichit
- Bo Phloi District, Kanchanaburi
- Bo Thong District, Chonburi
- Bueng Sam Phan District, Phetchabun
- Cha-Am District, Phetchaburi
- Chai Badan District, Lopburi
- Chok Chai District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Dan Chang District, Suphan Buri
- Dan Khun Thot District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Dan Sai District, Loei
- Hua Hin District, Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary
- Kaeng Khro District, Chaiyaphum
- Kaeng Krachan District, Phetchaburi
- Kanthararom District, Sisaket
- Kantharawichai District, Maha Sarakham
- Khao Ang Rue Nai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Khao Yai National Park
- Khlong Hat District, Sa Kaeo
- Khlong Luang District, Pathum Thani
- Khon Buri District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Khwao Sinarin District, Surin
- Klaeng District, Rayong
- Kui Buri District, Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Lan Sak District, Uthai Thani
- Lao Khwan District, Kanchanaburi
- Lom Kao District, Phetchabun
- Mae Mo District, Lampang
- Mueang Buriram District, Buriram
- Mueang Chaiyaphum District, Chaiyaphum
- Mueang Kamphaeng Phet District, Kamphaeng Phet
- Mueang Kanchanaburi District, Kanchanaburi
- Mueang Khon Kaen District, Khon Kaen
- Mueang Loei District, Loei
- Mueang Nakhon Pathom District, Nakhon Pathom
- Mueang Nakhon Ratchasima District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Mueang Nakhon Sawan District, Nakhon Sawan
- Mueang Nongbua Lamphu District, Nong Bua Lamphu
- Mueang Phetchaburi District, Phetchaburi
- Mueang Phichit District, Phichit
- Mueang Phrae District, Phrae
- Mueang Prachuap Khiri Khan District, Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Mueang Rayong District, Rayong
- Mueang Sakon Nakhon District, Sakon Nakhon
- Mueang Samut Prakan District, Samut Prakan
- Mueang Sisaket District, Sisaket
- Mueang Tak District, Tak
- Nam Nao National Park
- Nam Phong District, Khon Kaen
- Noen Maprang District, Phitsanulok
- Non Din Daeng District, Buriram
- Non Sung District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Non Suwan District, Buriram
- Non Thai District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Nong Bua Daeng District, Chaiyaphum
- Nong Chok District, Bangkok
- Nong Phai District, Phetchabun
- Nong Ya Plong District, Phetchaburi
- Ongkharak District, Nakhon Nayok
- Pak Chong District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Pak Tho District, Ratchaburi
- Pak Thong Chai District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Pang Sila Thong District, Kamphaeng Phet
- Phanat Nikhom District, Chonburi
- Phanom Sarakham District, Chachoengsao
- Phatthana Nikhom District, Lopburi
- Phimai District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Phlapphla Chai District, Buriram
- Pho Thale District, Phichit
- Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya Province
- Phrai Bueng District, Sisaket
- Phu Khiao District, Chaiyaphum
- Phu Khiao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Phu Wiang District, Khon Kaen
- Prachaksinlapakhom District, Udon Thani
- Prachantakham District, Prachinburi
- Pran Buri District, Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Prasat District, Surin
- Prathai District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Rasi Salai District, Sisaket
- Sakaerat Environmental Research Station
- Sam Ngao District, Tak
- San Kamphaeng District, Chiang Mai
- Sattahip District, Chonburi
- Satuek District, Buriram
- Si Maha Phot District, Prachinburi
- Si Racha District, Chonburi
- Sikhio District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Soi Dao District, Chanthaburi
- Suan Phueng District, Ratchaburi
- Sung Noen District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Suwannaphum District, Roi Et
- Tak Fa District, Nakhon Sawan
- Takhli District, Nakhon Sawan
- Tha Li District, Loei
- Tha Luang District, Lopburi
- Tha Takiap District, Chachoengsao
- Tham Pha Tha Phon Non-Hunting Area
- Thanyaburi District, Pathum Thani
- Thap Than District, Uthai Thani
- Thep Sathit District, Chaiyaphum
- Thung Yai Naresuan Wildlife Sanctuary
- Wat Bot District, Phitsanulok
- Watthana Nakhon District, Sa Kaeo
- Wiang Sa District, Nan
- Wichian Buri District, Phetchabun



