Species of Thailand
Indian pond heron
Ardeola grayii
William Henry Sykes, 1832
In Thai: นกยางกรอกพันธุ์อินเดีย
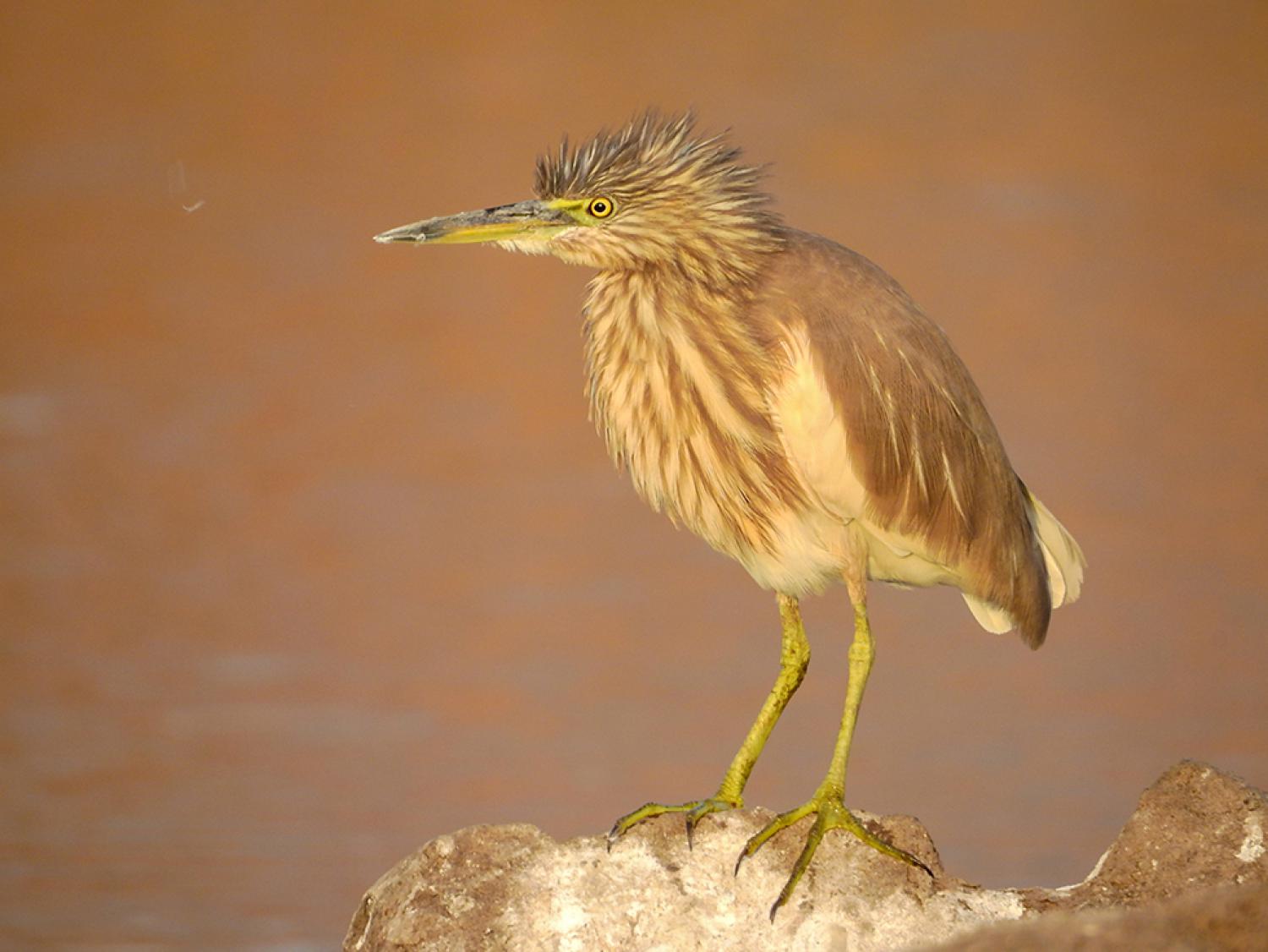
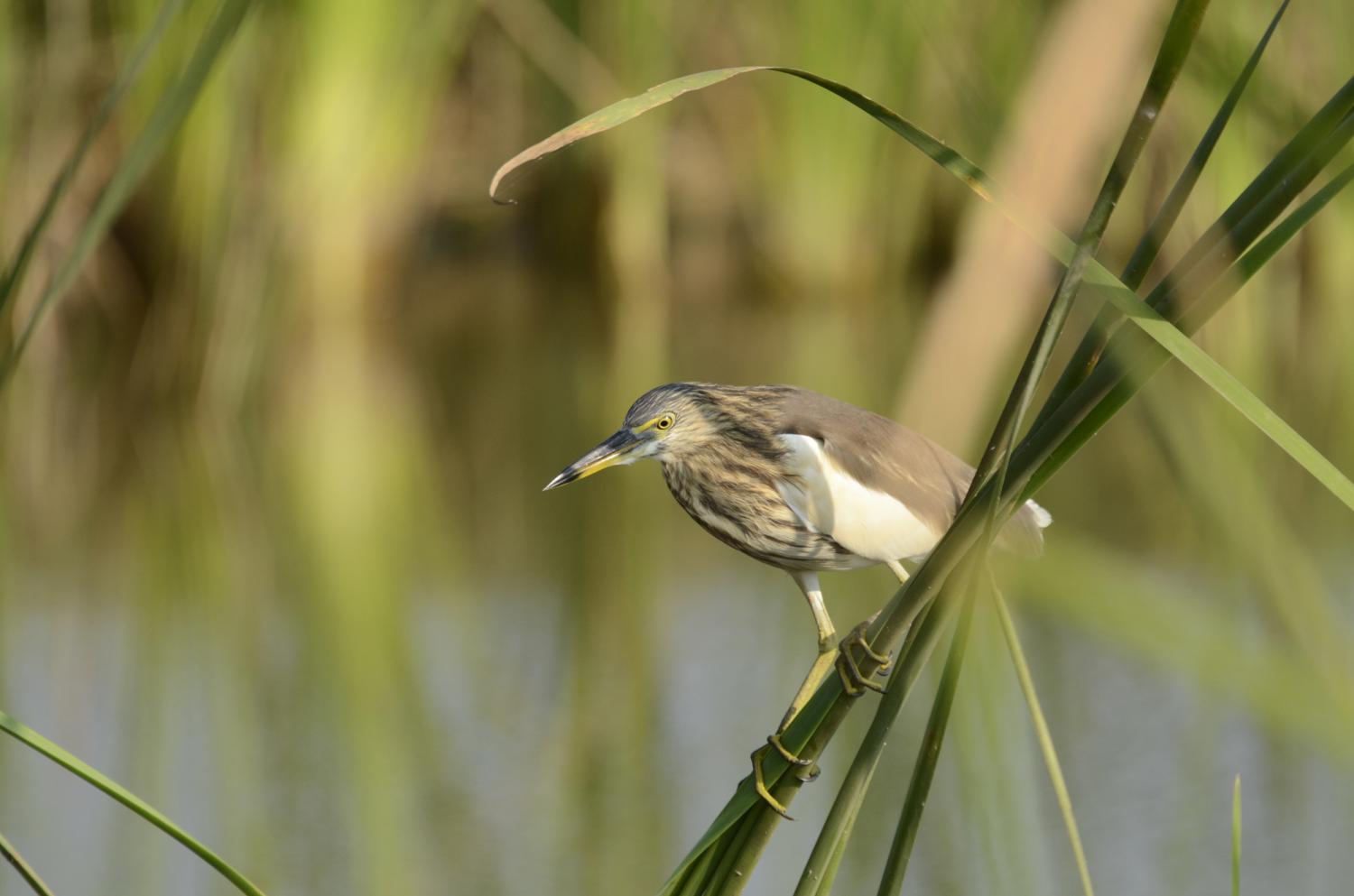
The Indian pond heron or paddybird (Ardeola grayii) is a small heron. It is of Old World origins, breeding in southern Iran and east to Pakistan, India, Burma, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka. They are widespread and common but can be easily missed when they stalk prey at the edge of small water-bodies or even when they roost close to human habitations. They are however distinctive when they take off with bright white wings flashing in contrast to the cryptic streaked olive and brown colours of the body. Their camouflage is so excellent that they can be approached closely before they take to flight, a behaviour which has resulted in folk names and beliefs that the birds are short-sighted or blind.
Description
They appear stocky with a short neck, short thick bill and buff-brown back. In summer, adults have long neck feathers. Its appearance is transformed from their dull colours when they take to flight, when the white of the wings makes them very prominent. It is very similar to the squacco heron, Ardeola ralloides, but is darker-backed. To the east of its range, it is replaced by the Chinese pond heron, Ardeola bacchus.
During the breeding season, there are records of individuals with red legs. The numbers do not suggest that this is a normal change for adults during the breeding season and some have suggested the possibility of it being genetic variants.
plumage has been noted. The race phillipsi has been suggested for the populations found in the Maldives, however this is not always recognized. It forms a superspecies with the closely related Chinese pond heron, Javan pond heron and the Madagascar pond heron.
They are usually silent but may give a harsh croak when flushed or near their nests.
This bird was first described by Colonel W. H. Sykes in 1832 and given its scientific name in honour of John Edward Gray. Karyology studies indicate that pond herons have 68 chromosomes (2N).
Behaviour and ecology
They are very common in India, and are usually solitary foragers but numbers of them may sometimes feed in close proximity during the dry seasons when small wetlands have a high concentration of prey. They are semi-colonial breeders. They may also forage at garbage heaps. During dry seasons, they sometimes take to foraging on well watered lawns or even dry grassland. When foraging, they allow close approach and flush only at close range. They sometimes form communal roosts, often in avenue trees over busy urban areas.
Food and feeding
The Indian pond heron's feeding habitat is marshy wetlands. They usually feed at the edge of ponds but make extensive use of floating vegetation such as water hyacinth to access deeper water. They may also on occasion swim on water or fish from the air and land in deeper waters. They have also been observed to fly and capture fishes leaping out of water.
Sometimes, they fly low over water to drive frogs and fishes towards the shore before settling along the shoreline.
The primary food of these birds includes crustaceans, aquatic insects, fishes, tadpoles and sometimes leeches (Herpobdelloides sp.). Outside wetlands, these herons feed on insects (including crickets, dragonflies and bees), fish (Barilius noted as important in a study in Chandigarh) and amphibians.
Breeding
The breeding season is prior to the monsoons. They nest in small colonies, often with other wading birds, usually on platforms of sticks in trees or shrubs. Most nests are built at a height of about 9 to 10 m in large leafy trees. The nest material is collected by the male while the female builds the nest. Three to five eggs are laid. The eggs hatch asynchronously, taking 18 to 24 days to hatch. Both parents feed the young. Fish are the main diet fed to young. Nest sites that are not disturbed may be reused year after year.
Movements
Nocturnal movements of pond herons have been noted along the coast near Chennai.
Mortality factors
They have few predators but injured birds may be taken by birds of prey.
An arbovirus "Balagodu", trematodes and several other parasites have been isolated from the species. Antibodies to Japanese encephalitis and West Nile virus has been detected in pond herons and cattle egrets from southern India. Traces of heavy metals acquired from feeding in polluted waters may be particularly concentrated in the tail feathers.
In culture
The habit of standing still and flushing only at the last moment has led to widespread folk beliefs that they are semi-blind and their name in many languages includes such suggestions. In Sri Lanka the bird is called kana koka which translates as "half-blind heron" in the Sinhala language. The phrase "bagla bhagat" has been used to describe a "wolf in sheep's clothing" or a heron appearing like a meditating saint.
During the height of the plume trade, feathers were collected from the "paddy bird" and exported to Britain.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Category / Seasonal Status
BCST Category: Recorded in an apparently wild state within the last 50 years
BCST Seasonal statuses:
- Resident or presumed resident
- Non-breeding visitor
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Pelecaniformes
- Family
- Ardeidae
- Genus
- Ardeola
- Species
- Ardeola grayii
Common names
- Thai: นกยางกรอกพันธุ์อินเดีย
Synonyms
- Ardeola leucoptera
Conservation status

Least Concern (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review the bird photos if wrong ones are used. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
- Ao Phang-Nga National Park
- Ban Laem District, Phetchaburi
- Bang Pu Recreation Centre
- Bangkok Province
- Khao Sam Roi Yot National Park
- Khao Yoi District, Phetchaburi
- Khlong Luang District, Pathum Thani
- Khura Buri District, Phang Nga
- Ko Man Nai
- Laem Pak Bia
- Mueang Chonburi District, Chonburi
- Mueang Phuket District, Phuket
- Mueang Samut Sakhon District, Samut Sakhon
- Mueang Surin District, Surin
- Mueang Tak District, Tak
- Pak Thale
- Samut Prakan Province
- Takua Pa District, Phang Nga
- Thale Noi Non-Hunting Area

